Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the Earth as a result of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, as well as man-made explosions. There are many types of seismic waves, each moving in different waves. The two main types of Seismic waves are called body waves and surface waves.
Body waves:
Body waves travel through the interior of the Earth, they have a higher frequency than Surface waves, and they arrive before the Surface waves are emitted by the earthquake. There are two types of Body waves: The Primary wave, and the Secondary wave. Each of them shakes the ground in different ways.
Primary waves
 The Primary Wave, or the P wave, is the fastest kind of Seismic wave and can travel from 5km to 8km per second, depending on the density of the medium. As a result, they are the first to be felt. P waves, unlike S waves, are able to travel through both solid and liquid layers of the Earth. Much like how Sound waves, P waves travel by compressing and dilating (Pushing and Pulling) the medium. The pushing and pulling produces a back and forward motion towards the direction of wave propagation, which is the direction that the energy is travelling in. Because of the pushing and pulling it does, the P Wave is also called the Compressional Wave.
The Primary Wave, or the P wave, is the fastest kind of Seismic wave and can travel from 5km to 8km per second, depending on the density of the medium. As a result, they are the first to be felt. P waves, unlike S waves, are able to travel through both solid and liquid layers of the Earth. Much like how Sound waves, P waves travel by compressing and dilating (Pushing and Pulling) the medium. The pushing and pulling produces a back and forward motion towards the direction of wave propagation, which is the direction that the energy is travelling in. Because of the pushing and pulling it does, the P Wave is also called the Compressional Wave.Image from http://allshookup.org/quakes/wavetype.htm
 Secondary Waves
Secondary WavesThe Secondary Wave, or S Wave, is the second wave you feel during an earthquake. It is slower than the P Wave and, unlike the P Wave, it can not travel through liquid mediums and can only travel through solid ones. Seismologists were able to conclude that the Earth's outer core is a liquid. They were able to do this because P Waves could be felt of the opposite side of the earth but S Waves could not. S waves move the rock particles up and down, or side to side, perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation.
Image from https://www.thinglink.com/scene/581579679287214082
Surface waves:
As the name suggests, Surface waves travel only through the crust. They are of a lower frequency than body waves and arrive after the Body waves. Although they arrive after the Body waves, almost the entirety of the damage caused by an earthquake is the result of Surface waves. There are two types of Surface waves: the love wave, and the Rayleigh wave.
 Love wave
Love waveIn 1911, a British mathematician named A.E.H. Love worked out the mathematical model for this kind of Surface wave. As a result, this wave was given the name 'Love wave'. The S wave moves the ground either up and down, or side to side. The Love wave is basically the same but it only moves it from side to side, not up and down. The Love wave is also the fastest kind of surface wave. They generally travel from 2 to 6 kilometers per second.
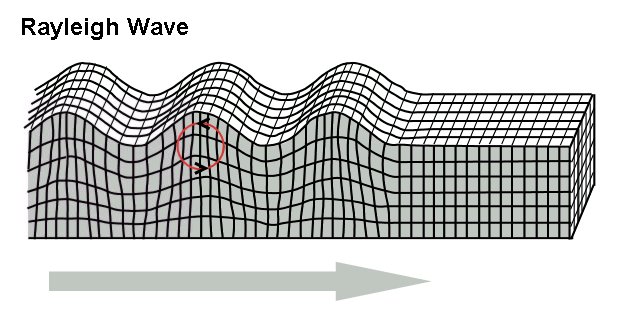 Rayleigh wave
Rayleigh waveThe Rayleigh wave is the other kind of Surface wave. It was named for John Willian Strutt, Lord Rayleigh, who, in 1885, mathematically predicted the existence of this kind of wave. Rayleigh waves are also known as ground roll because it rolls. Similar to ripples and waves on the ocean surface, Rayleigh waves spread through the ground as ripples, moving both vertically and horizontally. Most of the shaking during an earthquake is because of the Rayleigh wave.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.